Preserving insulin from degradation is of major interest to endocrinologists, molecular biologists and protein biochemists. Indeed, the therapeutic efficacy of a drug used by millions of people living with diabetes around the world is at stake.

The vast majority of the 420 million people with diabetes live in low- and middle-income regions. Of these, 9 million live with type 1 diabetes. A further 63 million have type 2 diabetes requiring insulin treatment, only half of whom have access to it.
Insulin manufacturers routinely advise that unopened vials of insulin should be stored in the refrigerator at a temperature between 2°C and 8°C, and that an already opened vial should not be exposed to temperatures above 25°C-30°C during its shelf life, which, depending on the product, can vary from ten days to eight weeks. Manufacturers recommend that insulin removed from the fridge should be disposed of within a specified period, whether or not the vial has already been opened and not yet used. For most products, this period is four weeks.
To complicate matters, the instructions for use recommend storing insulin in the refrigerator or at room temperature. Insulin should be stored at room temperature, between 15°C and 30°C in the United States and below 30°C in the European Union.
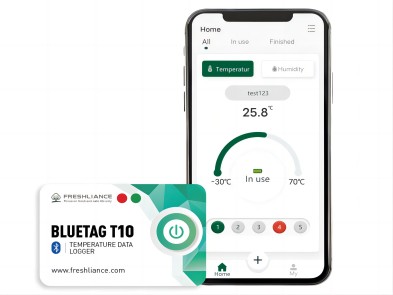
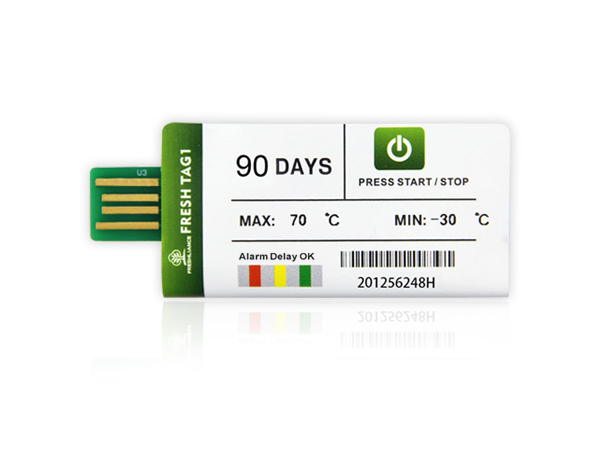
Blue Tag T10 insulin is a versatile Bluetooth temperature data logger. It features high-resolution temperature ranges from 2°C to +8°C. It can be used in confined spaces where compliance monitoring is required. All parameters can be set via APP on the cell phone.
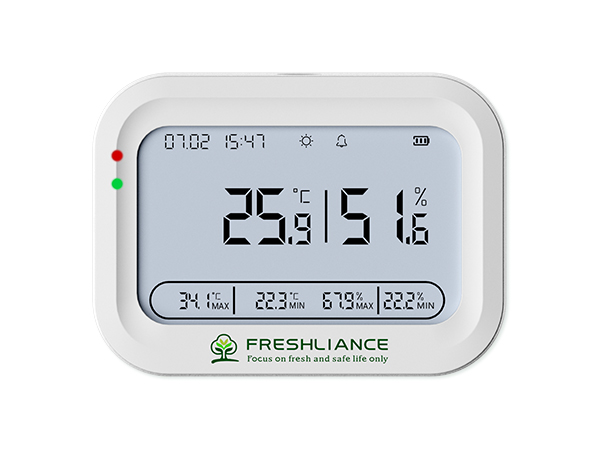
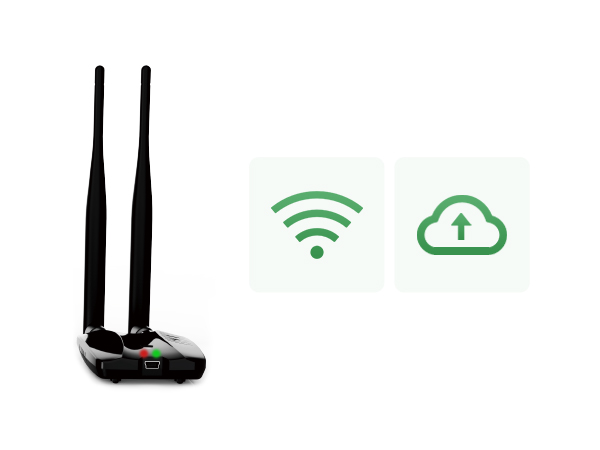
You can place the Bluetooth temperature logger next to the insulin in the refrigerator. Connect to Wi-Fi and get temperature data directly from your phone, or place the Bluetooth temperature logger in your insulin or growth hormone bag on the move and read temperature data directly via Bluetooth.

 English
English Español
Español Русский
Русский Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch عربي
عربي 中文
中文



